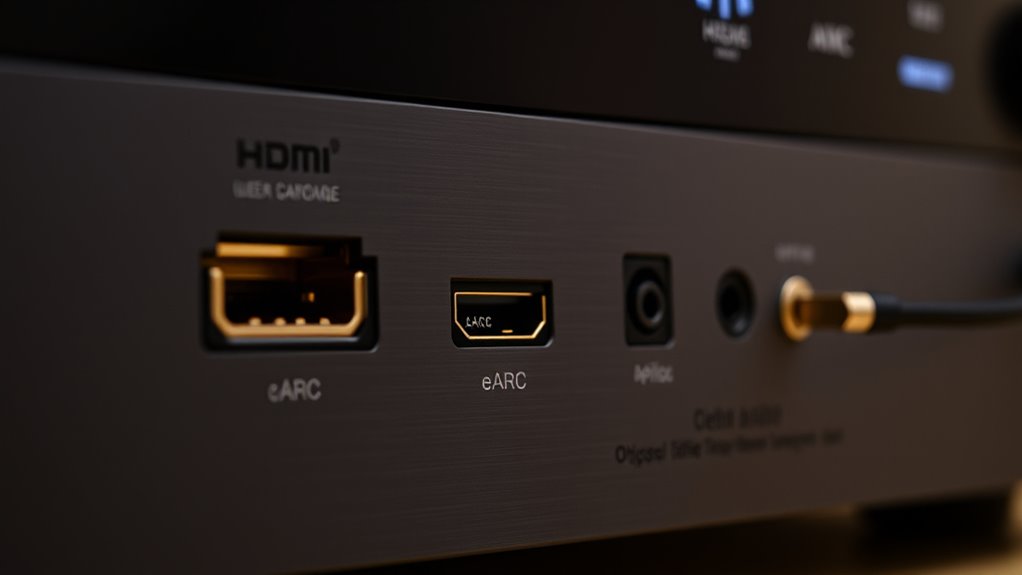
HDMI ARC, eARC, and optical are different ways to connect your TV to audio devices. HDMI ARC is common and easy, suitable for basic audio like Dolby Digital, but has bandwidth limits. eARC is a newer, better option that supports high-resolution, immersive sounds like Dolby Atmos. Optical cables are simple and immune to interference but can’t handle high-quality formats. To maximize sound quality, understanding these differences helps you choose the best setup—let’s explore further.
Key Takeaways
- HDMI ARC uses a single HDMI cable to transmit compressed audio, suitable for basic setups, while eARC supports uncompressed, high-resolution, immersive audio formats.
- eARC offers higher bandwidth than HDMI ARC and optical, enabling the transmission of formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS:X for superior sound quality.
- Optical cables are limited to compressed audio formats and cannot support high-resolution or object-based audio, unlike HDMI ARC and eARC.
- HDMI ARC and eARC require compatible hardware, with eARC needing specific support on both TV and audio devices, whereas optical is widely compatible but less advanced.
- For future-proof, high-fidelity audio setups, eARC is recommended due to its support for emerging high-quality audio formats and better synchronization.
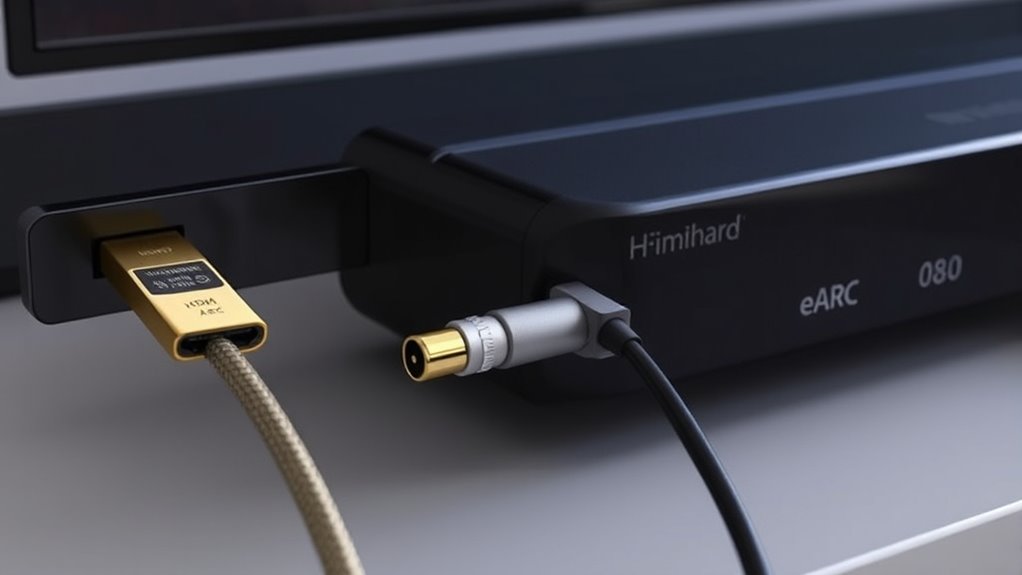

When choosing how to connect your audio devices, understanding the differences between HDMI ARC, eARC, and optical cables is essential. Each option has its unique capabilities and limitations, which can affect your overall audio experience. HDMI ARC (Audio Return Channel) was introduced to simplify connections by allowing your TV to send audio back to your soundbar or AV receiver through a single HDMI cable. It’s a convenient feature, but it has bandwidth restrictions that limit the quality and formats you can transmit. Typically, HDMI ARC supports compressed audio formats like Dolby Digital and DTS, which are suitable for most standard setups but don’t deliver the highest fidelity or support newer immersive formats.
eARC (enhanced Audio Return Channel) is an upgrade to HDMI ARC, designed to overcome these limitations. It offers considerably higher bandwidth, allowing for the transmission of uncompressed, high-resolution audio, including Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD Master Audio, and object-based formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X. If you want the best possible sound quality and future-proof your setup, eARC is the better choice. It also improves synchronization between audio and video, reducing lag and ensuring a seamless experience. The key point is that eARC requires compatible hardware on both your TV and audio device, so just having an HDMI cable isn’t enough—you need to ensure the devices support eARC.
Optical cables, also known as TOSLINK, are another common method for transmitting audio signals. They use light to transfer digital audio, which means they’re immune to electrical interference and can produce clear sound. Optical cables are straightforward to set up and are compatible with many TVs and soundbars. However, they have limited bandwidth compared to HDMI connections, which restricts them to supporting compressed audio formats and prevents transmission of high-resolution or object-based audio formats. This makes optical cables less suitable if you’re aiming for the highest sound quality or want to experience immersive audio formats. Additionally, security vulnerabilities in new audio technologies can pose risks if not properly managed.
In terms of practical differences, if your devices support HDMI ARC, it’s a good, simple option for basic setups. If you want the highest quality and future compatibility, eARC is ideal, provided your equipment supports it. Optical might still be useful if you don’t have HDMI ports or need a quick, interference-free connection, but it’s generally less capable in handling advanced audio formats. Furthermore, understanding the compatibility requirements is crucial to ensure your setup works seamlessly. It’s also worth noting that additional features like HDMI-CEC can enhance your user experience by enabling device control through a single remote. Ultimately, your choice depends on your equipment and your desire for audio fidelity. Knowing these differences helps you make an informed decision to get the best sound from your home entertainment system.

Yaber K300s Ultra Short Throw Projector, 4K Support Triple Laser Projector, 100" Image at 9", Dolby Vision, 150% NTSC, Google TV, 30W JBL Speaker, for Home Theater Gaming
[Ultra Short Throw & Space-Saving Design] Experience a 100-inch giant screen from just 9 inches away with the...
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Connect Multiple Devices Simultaneously Using These Audio Connections?
You can’t connect multiple devices directly through a single HDMI ARC, HDMI eARC, or optical port. These connections typically support only one device at a time. However, you can use a switch or receiver with multiple inputs to connect several devices, then output to your TV or sound system. This setup allows you to switch between devices easily, giving you more flexibility without sacrificing audio quality.
Which Connection Offers the Best Sound Quality for Gaming?
Imagine you’re a music conductor, guiding a symphony with precision. For gaming, HDMI eARC is your best baton, delivering the purest, most detailed sound. It handles high-bitrate audio formats, making explosions and footsteps crystal clear. Optical is like a simple flute—good but limited. HDMI ARC offers decent sound, but eARC takes the lead, ensuring every sound detail immerses you fully in your gaming experience.
Are There Compatibility Issues Between Different Brands’ HDMI ARC and Earc Ports?
You might wonder if different brands’ HDMI ARC and eARC ports work together smoothly. Generally, compatibility isn’t a big issue, but it’s best to verify if your devices support the same HDMI standards, like HDMI 2.1 for eARC. Some brands may have proprietary features that cause minor hiccups. To ensure seamless audio, use devices from reputable brands and keep firmware updated.
How Do I Troubleshoot Common Audio Synchronization Problems?
Ever feel like your audio’s stuck in a time warp? To troubleshoot sync issues, start by checking all connections to make certain they’re secure. Restart your devices, update firmware, and set your TV and sound system to the same audio output. If problems persist, try switching between HDMI ARC, eARC, or optical cables. Sometimes, a simple reset or cable swap is all it takes to restore perfect harmony.
Do These Connections Support High-Resolution Audio Formats Like Dolby Atmos?
You’re wondering if HDMI ARC, eARC, or optical connections support high-resolution audio like Dolby Atmos. HDMI ARC offers limited support for Atmos, but eARC fully supports it, delivering immersive sound with higher bandwidth. Optical connections, however, don’t support Dolby Atmos or other high-res formats due to bandwidth limitations. For the best experience, use HDMI eARC for Dolby Atmos and other high-res audio formats.

Official Licensed Google TV Smart Projector, HAPPRUN 4K UHD Home Theater with Dolby Sound, Wi-Fi & Bluetooth, Built-in Streaming Apps, Compatible with Games Consoles & Smartphone, Indoor & Outdoor Use
[ Built-in Official Licensed Google TV ] - Without additional equipment, the smart projector can directly access Netflix,...
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Conclusion
As you navigate your audio setup, remember that choosing between HDMI ARC, eARC, or optical is like selecting the right brush for your masterpiece. Each connection type offers its unique touch—ARC’s simplicity, eARC’s high fidelity, and optical’s compatibility. Like mastering a symphony, understanding these options helps you craft a seamless soundscape. So, pick what suits your needs, and let your home theater sing in perfect harmony—your personal stage for unforgettable moments.

Hisense PL2, Ultra Short Throw Home Theater Laser Projector, 80” – 150”, 4K UHD, 2,700 Lumens, 3000:1 Contrast, Dolby Vision & Atmos, 3D, Google TV, WIFI 6E
【X-Fusion Technology】With X-Fusion laser light, Laser Cinema has a uniquely cinematic feel. X-Fusion Laser Technology utilises a precise...
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.

ViewSonic LS901-4K UHD 4K Laser Projector with 5500 Lumens, 1.7X Optical Zoom, 4K HDR/HLG Support, 4 Corner Adjustment, H/V Keystone, 360 Degrees Projection for Home Theater and Commercial Venues
4K Home Theater Laser Projector: UHD (3840x2160p) 4K resolution with a 1.2-2.0 throw ratio and 5,500 ANSI lumens,...
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.